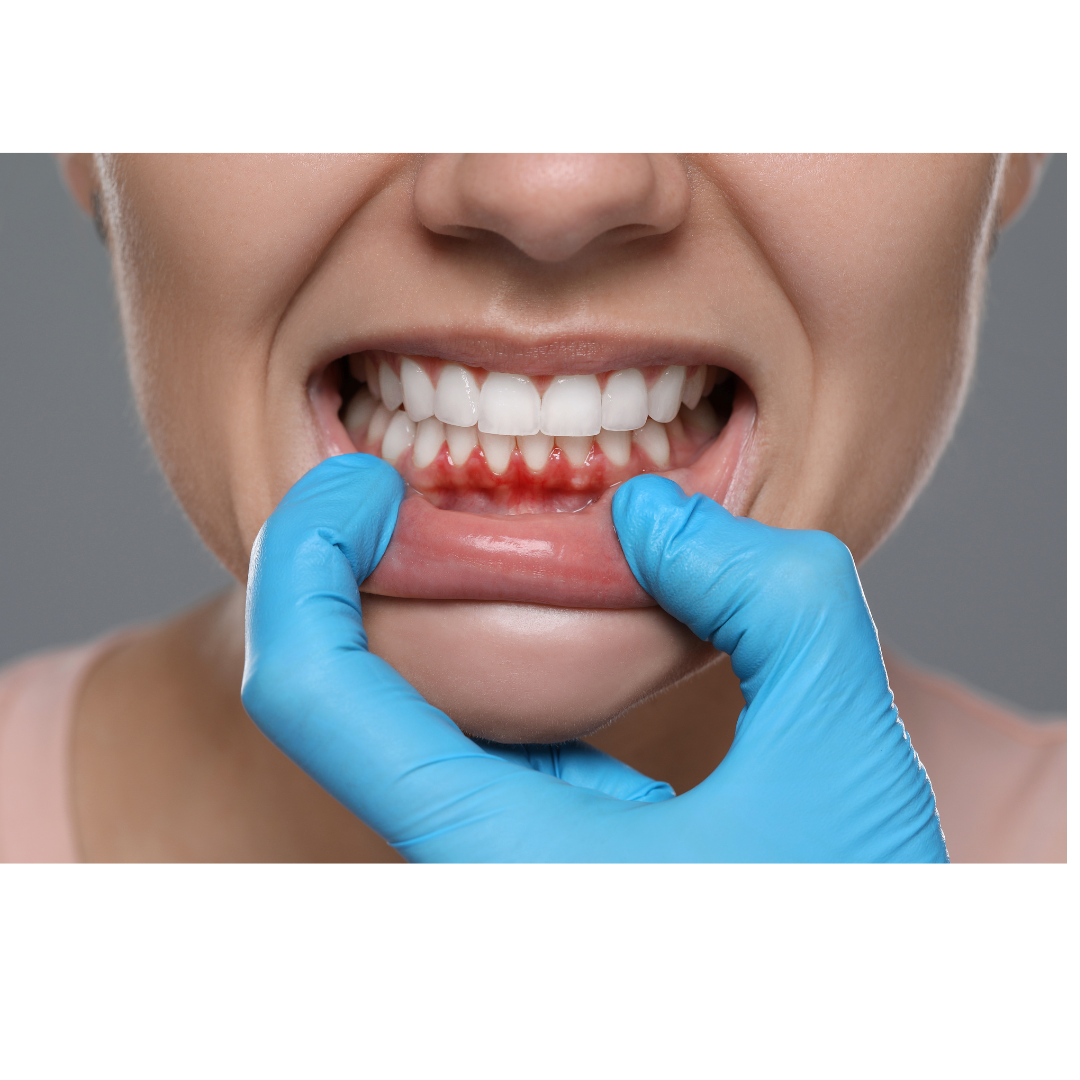
Gum recession, the tissue around the teeth is pulled back to protect the tooth roots is a common gum problem that can lead to tooth sensitivity, infections and tooth loss. Left untreated, it can lead to tooth sensitivity, infections and tooth loss.
Why does gingival recession occur?
1. Wrong Brushing Technique: Brushing teeth with hard movements can damage the gums.
2. Gum Diseases: Infections such as gingivitis and periodontitis are the main causes of gum recession.
3. Genetic Factors: If there are gum problems in the family, the risk may be higher.
4. Smoking: Tobacco products weaken the gums by reducing blood flow to them.
5. Faulty Dentures or Braces: Inappropriate dental treatments can cause gum recession.
Symptoms of Gum Recession
– The roots of the teeth become visible.
– Hypersensitivity of the teeth (especially with hot and cold foods).
– Bleeding and redness of the gums.
– Bad breath.
– Teeth appear longer than normal.
Treatment Methods
Early diagnosis is important in the treatment of gum recession. Treatment options are as follows:
– Gingival Graft: Healthy tissue is added to the receding area.
– Deep Cleaning (Curettage and Root Correction): Plaque and tartar accumulated under the gums are removed.
– Laser treatment: The infected tissue is removed in a gentle and painless way.
– Medical treatment: The infection can be controlled with medicines.
What should be done to prevent gum recession?
– Brush your teeth gently with a soft brush.
– Make flossing and mouthwash a habit.
– Go to the dentist every 6 months.
– Pay attention to a balanced diet; consume foods that are beneficial for gum health, such as vitamin C.
– Quit smoking and tobacco products.
Things to Consider After Treatment
If oral hygiene is not taken care of after treatment , gum problems may recur. To protect gum health:
– Avoid acidic and hard foods.
– Use special toothpastes recommended by your dentist.
– Do not neglect your post-treatment controls.